Documentation
Overview of Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
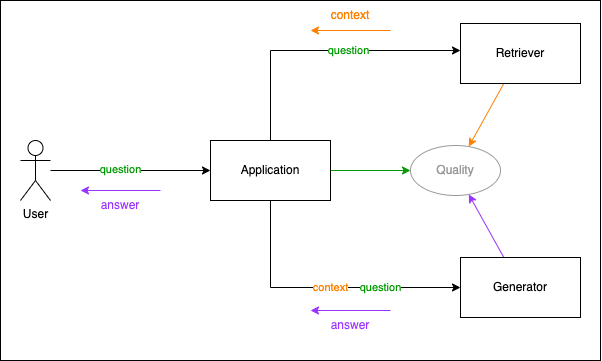
This is an overview of the Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) system. The system consists of three parts: the retriever, the generator, and the quality component. The retriever is responsible for retrieving relevant chunks from a corpus of documents. The generator is responsible for generating an answer based on the context and the question. The quality component is responsible for determining the quality of the generated text and the retrieved chunks, all related to the question from the user.
The Application receives the question from the user. The question is provided to the retriever. The retriever obtains relevant chunks and constructs the context out of those chunks. Next, the context is provided to the generator together with the question. The generator returns an answer, which is returned to the user. The quality component receives the question, the chunks, the context and the answer. It returns a quality score for the the retrieved chunks in relation to the question. Next the quality component uses an LLM to determine the quality of the answer in relation to the question. The quality component also uses an LLM to determine the quality of the answer in relation to the context. This is to prevent hallucination.
Below you find more detailed information about the different components of the system.
The retrieval part of the system
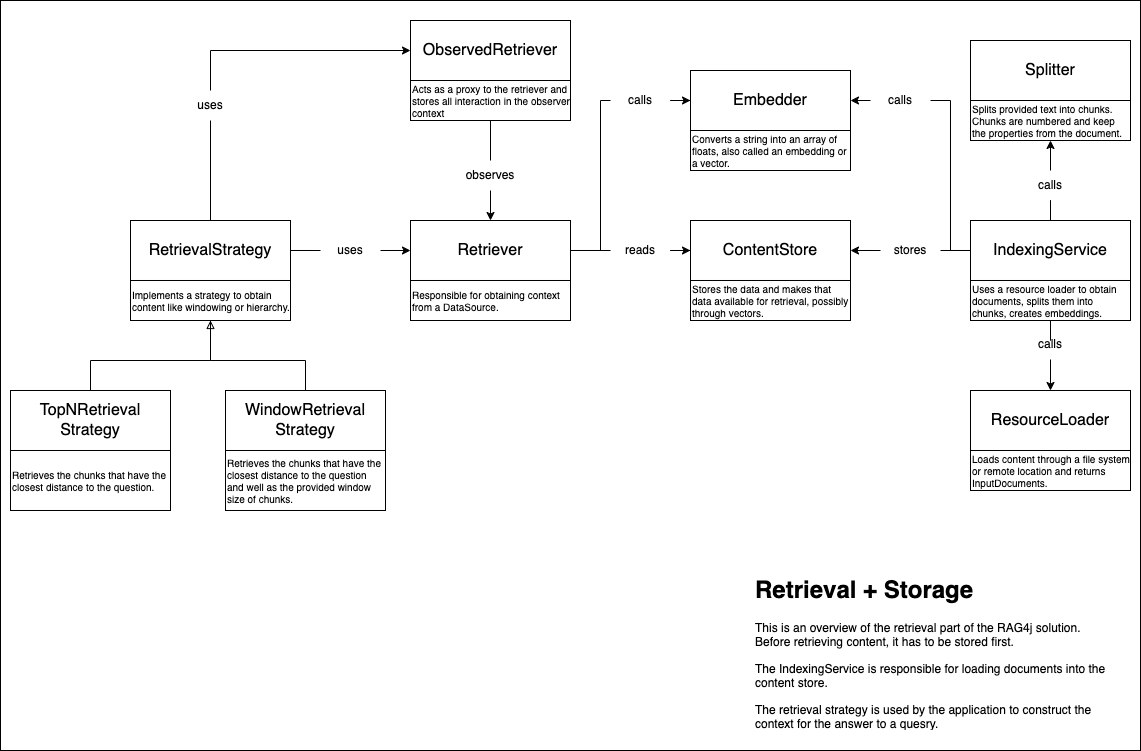
An important part of the Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) system is the retriever. The retriever is responsible for retrieving relevant chunks from a large corpus of documents. Use the RetrievalStrategy to construct a context from the retrieval output. The context size is influenced by the chunk size, the amount of chunks to use, and the retrieval strategy. The Top-N retrieval strategy just returns the number of requested chunks as the context. The window retrieval strategy uses a window of chunks around the matched chunk from the same document.
To be able to retrieve chunks from a corpus, the corpus needs to be indexed. The IndexingService uses a ResourceLoader to load the content. With a splitter and an embedder, vectors are created and stored in the content store.
Important classes of the retrieval part
- The
Retrieveris responsible for retrieving relevant chunks from a large corpus of documents. It contains one method to search for relevant chunksfind_relevant_chunksorfindRelevantChunks. The method accepts the question to to use for finding relevant chunks and the number of chunks to retrieve. The retriever has additional methods that support retrieval strategies. You can obtain a chunk by document id and chunk id through get_chunk or getChunk. You can also loop over all the chunks available in the retriever through loop_over_chunks or loopOverChunks. - The
RetrievalStrategyis responsible for constructing a context from the retrieval output. The context size is influenced by the chunk size, the amount of chunks to use, and the retrieval strategy. The Top-N retrieval strategy just returns the number of requested chunks as the context. The window retrieval strategy uses a window of chunks around the matched chunk from the same document. - The
IndexingServiceis responsible for indexing the corpus. It uses aContentReaderto load the content. With aSplitterand anEmbedder, vectors are created and stored in the content store. - The
ContentReaderis responsible for loading the content from the corpus. The content reader works best with the IndexingService. An example is theVasaContentReaderwhich is used to load the Vasa corpus available in the provided jsonl file. - The
Splitteris responsible for splitting the content into chunks. The splitter is used by the IndexingService to split the content into chunks. A number of splitters are available. TheMaxTokenSplitterthat splits the chunks into chunks with a maximum amount of tokens. Then there is anOpenNLPSentenceSplitterin Java, and aSentenceSplitterin Python that splits the content into sentences. TheSingleChunkSplitterdoes not really split the text into chunks, it creates one Chunk. - The
Embedderis responsible for creating vectors from the chunks. There are different embedders. Most of the Embedders use aModelto create vectors from the tokens. We have a local running model,AllMiniLmL6V2QEmbedderin Java orOnnxEmbedderin Python. There is also anOpenAIEmbedderthat uses the OpenAI API to create vectors from the tokens. - The
ContentStoreis responsible for storing the vectors. The ContentStore is used by the IndexingService to store the vectors. The ContentStore is used by the Retriever to retrieve the vectors. We have two ContentStores available. TheInternalContentStorethat stores the vectors in memory. TheWeaviateContentStorethat stores the vectors in a Weaviate.
The generation part of the system
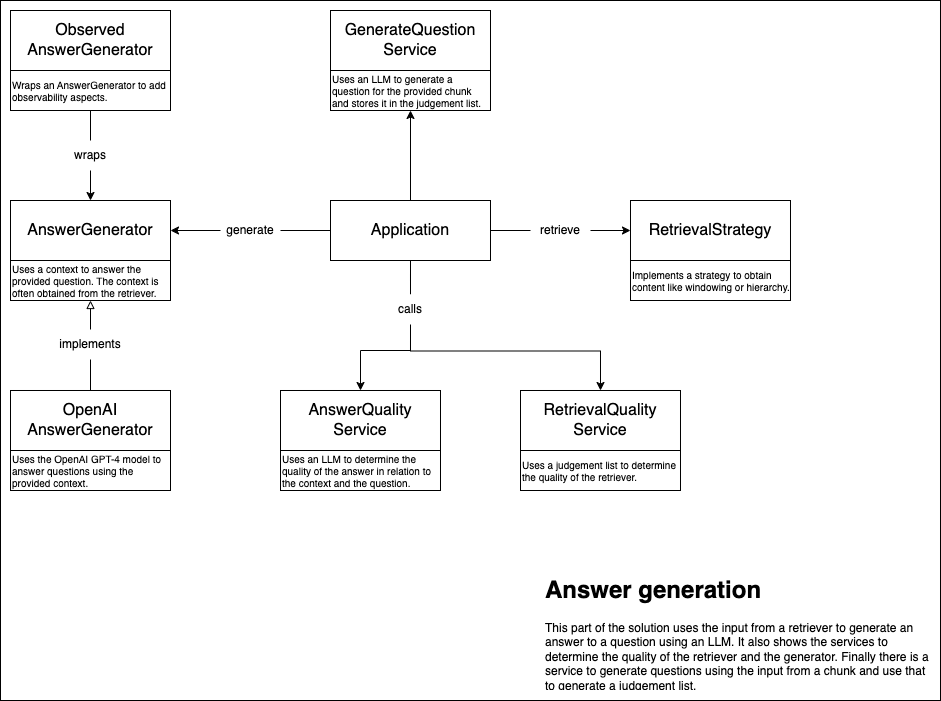
The generator is responsible for generating an answer based on the context and the question. The generator uses a model to generate text. In our case we only have the OpenAI LLM. The application uses the retrieval strategy to obtain relevant chunks. The chunks are used to construct the context. The context is provided to the generator together with the question.
The quality component is responsible for determining the quality of the generated text. There is a quality if the answer really answers the question and if the answer is deduced from the context and not made up by the LLM. There is also a retriever quality, this makes use of the generated judgement list to determine the quality of the retrieved chunks.
Important classes of the generation part
- The
Applicationis the starting point for our RAG system. It receives the question from the user, obtains the context from the retriever, sends the question plus context to the generator and obtains an answer from the generator.The project contains a lot of sample applications. Some do only part of this flow, others do the complete flow. - The
AnswerGeneratoris responsible for generating an answer based on the context and the question. The generator uses a model to generate text. In our case we only have theOpenaiAnswerGenerator. The prompt to generate the answer is available in the code and can easily be adjusted.
The quality component of the system
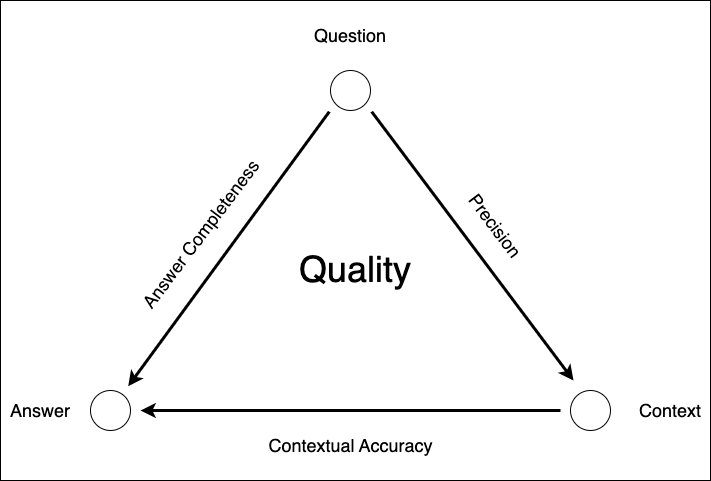
The quality component is responsible for determining the quality of the generated text and the retrieved chunks, all related to the question from the user. There are three metrics to determine the overall quality of your RAG:
- The precision: the quality of the results of the retriever in relationship to the question. In our case, we have a judgment list with questions and the optimal chunk/result for that question. This list is created using synthetic questions generated by an LLM. From each chunk, we generate a question using an LLM. Next, the questions go through the retriever; they should return the chunk from which the question was generated. The precision is a score between 0 and 1, where one is perfect.
- Contextual Accuracy: the quality of the answer in relationship to the context. The context is constructed from the chunks retrieved by the retriever. The generator generates the answer. The answer should be deduced from the context. The contextual accuracy is between 1 and 5, where five is perfect. This score is obtained through the LLM by asking the LLM about the quality of the answer concerning the context.
- Answer Completeness: the quality of the answer in relationship to the question. The generator generates the answer. The answer should be deduced from the question. The answer accuracy is a score between 1 and 5, where five is perfect. The score is obtained through the LLM by asking the LLM about the quality of the answer concerning the question.
Important classes of the quality part
The quality implementation is divided over two services. The RetrieverQualityService and the AnswerQualityService. The RetrieverQualityService is responsible for determining the quality of the retrieved chunks. The AnswerQualityService is responsible for determining the quality of the generated text. The quality of the answer is related to the question as well as the context.
- The
RetrievalQualityServiceis responsible for determining the quality of the retrieved chunks. The quality of the retrieved chunks is determined by the precision. The precision is a score between 0 and 1, where one is perfect. The precision is determined by theJudgmentListand theRetriever. TheJudgmentListcontains questions and the optimal chunk/result for that question. This list is created using synthetic questions generated by an LLM. From each chunk, we generate a question using an LLM. Next, the questions go through the retriever; they should return the chunk from which the question was generated. - The
AnswerQualityServiceis responsible for determining the quality of the generated text. The quality of the answer is related to the question as well as the context. The AnswerQualityService uses an LLM to determine the quality of the answer in relation to the question and the context. It asks the LLM to rate the answer with a score from 1 to 5, where 1 is bad and 5 is perfect.
In Java a LocalThread is use to gather additional information about the observer. The LocalThread is managed by the RAGTracker, data is stored in the RAGObserver. In python we also use the rag_tracker, in this case it manages an instance of the RAGObserver using a global variable.
Extra: Generating a judgment list
To review the quality of the retriever, we need a judgment list. The judgment list contains questions and the optimal chunk/result for that question. This list is created using synthetic questions generated by an LLM.
- The
QuestionGeneratorServiceis responsible for generating a question for each available chunk in the ContentStore. The combination of generated questions, and the originating chunk are stored in a jsonl file. Looping over all the chunks is done using theloop_over_chunksmethod of the retriever. Each chunk is provided to the question generator to generate a question from that chunk. - The
QuestionGeneratoraccepts a context to generate a question. At the moment there is one implementation available, theOpenaiQuestionGenerator. The question generator uses the OpenAI API to generate a question from the context. The question generator is used by theQuestionGeneratorServicethat uses the GPT-4 or other model to generate a question. Of course this is done using a prompt.
